New study on the size-dependent efficacy of hemostatic nanoparticles
A new analysis offers guidance on the size of nanoparticles that could be most effective at stopping internal bleeding. Image: Christine Daniloff, MIT
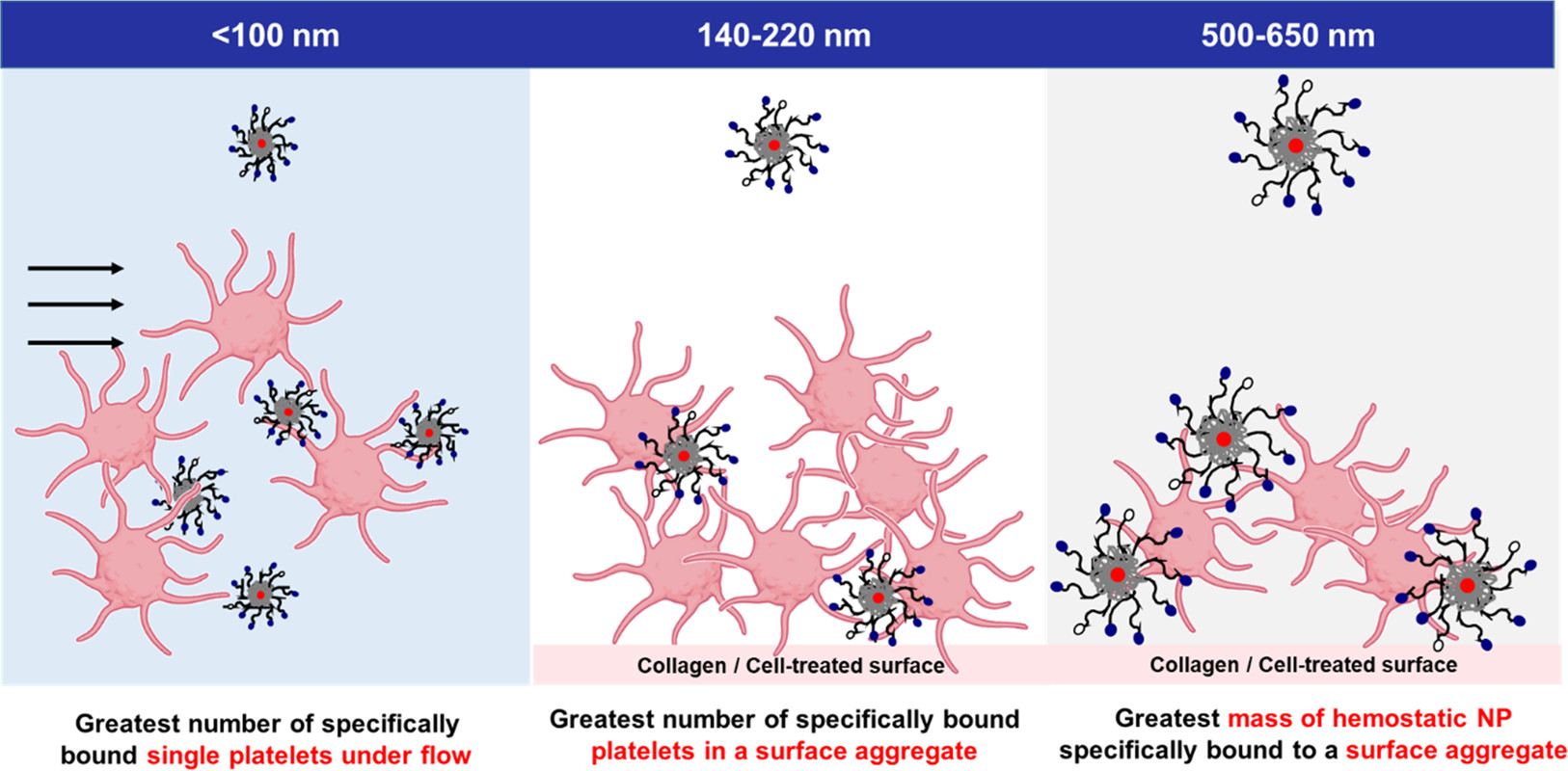
Summary of In Vitro Experimental Results for Particle Sizes to Be Tested in the Lethal Injury Model — Sub-100-nm nanoparticles resulted in the greatest number of specifically bound platelets under flow, intermediate-sized nanoparticles resulted in the greatest number of platelets in a platelet–particle surface aggregate, and the largest particles resulted in the greatest polymer mass accumulation onto platelet–particle surface aggregates. Adapted from Biorender. Image: Celestine Hong, Osaid Alser, Anthony Gebran, Yanpu He, Wontae Joo, Nikolaos Kokoroskos, George Velmahos, Bradley D. Olsen, and Paula T. Hammond, ACS Nano 2022 16 (2), 2494-2510.

