Breakthrough in 2-D polymerization yields ultra-strong, lightweight material
The new material is a two-dimensional polymer that self-assembles into sheets and could be used as a lightweight, durable coating for car parts or cell phones, or as a building material for bridges or other structures. Image: polymer film courtesy of the researchers; Christine Daniloff, MIT
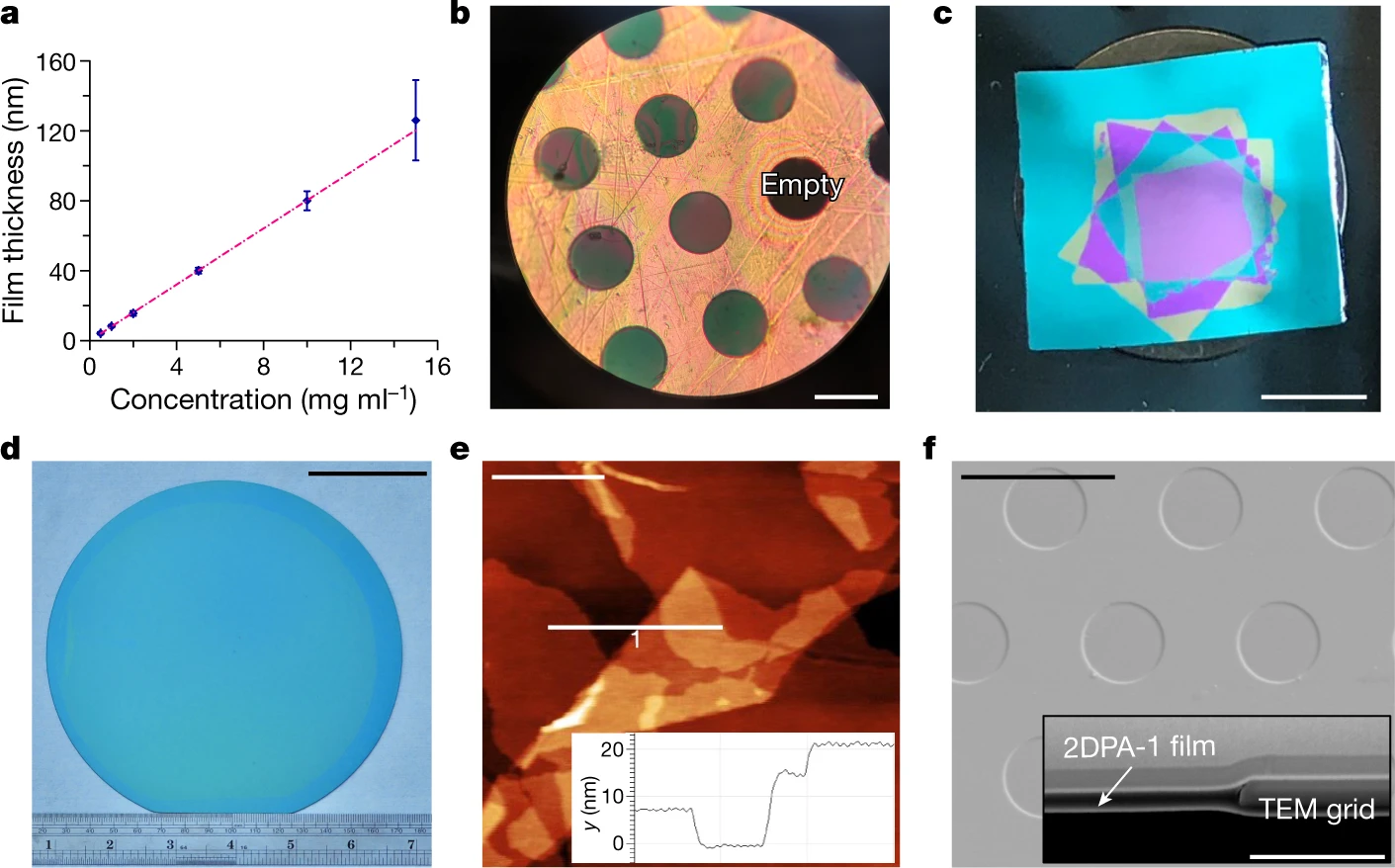
Characterization of 2DPA-1 nanofilms — a, Plot of nanofilm thickness against solution concentration of spin-coating. b, Transferred 2DPA-1 films across 30-μm holes. c, A five-layer film stack on a SiO2/Si wafer. d, A 7-nm thick transferred film on a 6-inch (150 mm) wide SiO2/Si wafer. e, Cracks, wrinkles and folds are observed at the film edge of d. The height profile of line 1 is shown in the inset. f, SEM images of a suspended 2DPA-1 film on an Si3N4 TEM grid. Inset, a cross-sectional view of a hole after focused ion beam (FIB) cutting. Scale bars are 30 μm (b), 5 mm (c), 5 cm (d), 1 μm (e) and 10 μm and 1 μm (f and inset, respectively). Image: Zeng, Y., Gordiichuk, P., Ichihara, T. et al. Irreversible synthesis of an ultrastrong two-dimensional polymeric material. Nature 602, 91–95 (2022).

